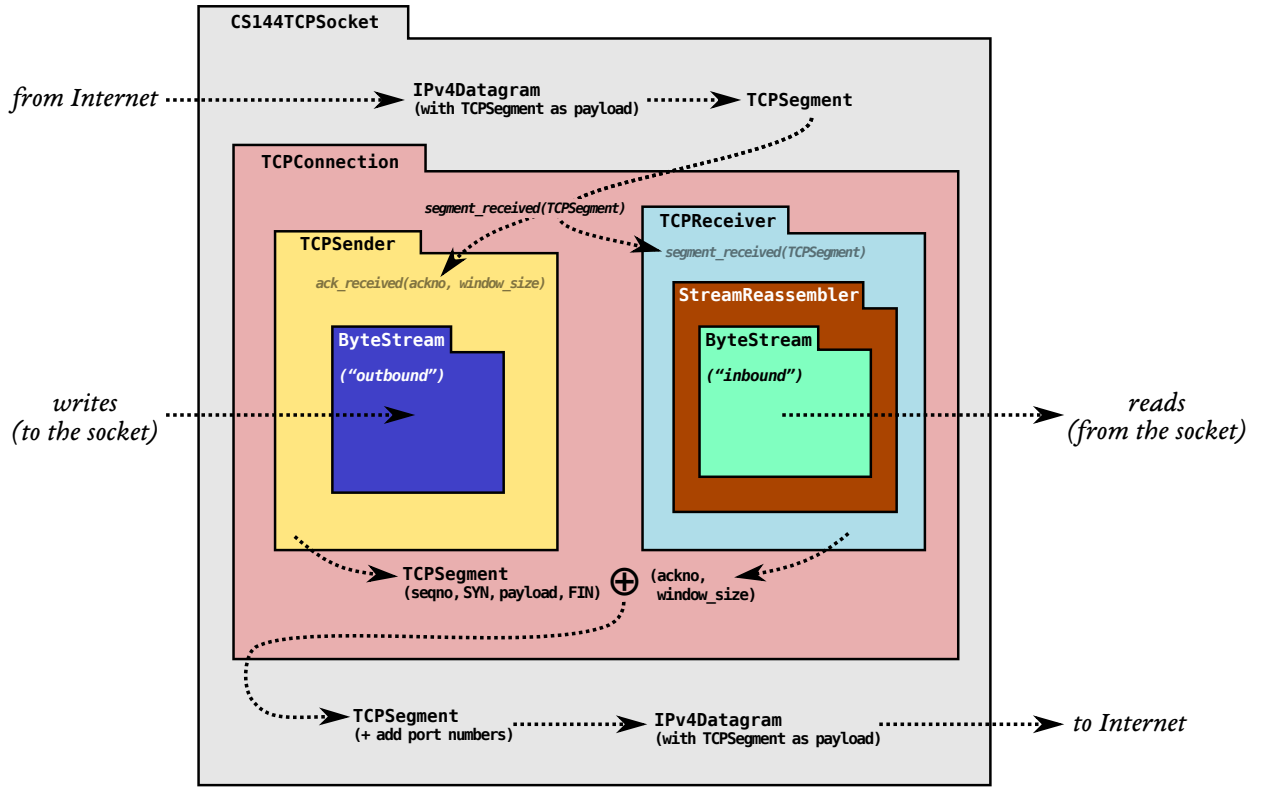
CS144 Lab 1 Stream Reassembler :
实现 stream Reassembler 流组装器,也就是流重组器
 {:height 480, :width 750}
不同协议的 ack 收发方式不同,在这边默认是 ack 乱序收发,这里关系不大。只是需要把在空间内能存的存了。但是如果卡了一个包没收那就不能收了
{:height 480, :width 750}
不同协议的 ack 收发方式不同,在这边默认是 ack 乱序收发,这里关系不大。只是需要把在空间内能存的存了。但是如果卡了一个包没收那就不能收了
Reassembler
void Reassembler::insert( uint64_t first_index, string data, bool is_last_substring )
插入 byte,这个在处理一些长度是很麻烦。(因为长度超过 capacity 就会丢弃)
一些问题
左值引用和右值引用是啥?
explicit Reassembler( ByteStream&& output ) : output_( std::move( output ) )
在实际场景中,右值引用和std::move被广泛用于在STL和自定义类中实现移动语义,避免拷贝,从而提升程序性能。 在没有右值引用之前,一个简单的数组类通常实现如下,有构造函数、拷贝构造函数、赋值运算符重载、析构函数等。深拷贝/浅拷贝在此不做讲解。
一句话总结右值引用:可移动对象在<需要拷贝且被拷贝者之后不再被需要>的场景,建议使用std::move触发移动语义,提升性能。
example:
template<typename T>
void func(T& param) {
cout << "传入的是左值" << endl;
}
template<typename T>
void func(T&& param) {
cout << "传入的是右值" << endl;
}
int main() {
int num = 2019;
func(num);
func(2019);
return 0;
}
 {:height 208, :width 749}
{:height 208, :width 749}
reassembler.cc
#include "reassembler.hh"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void Reassembler::insert( uint64_t first_index, string data, bool is_last_substring )
{
bool write_flag = false;
uint64_t capacity = output_.writer().available_capacity();
if (first_index + data.size() - _offset >= _reasse_vector_size)
{
buffer_update();
}
for(uint64_t i = 0; i < data.size(); i++)
{
// 如果即将 push 的超过 buffer 的大小,则直接丢弃
if (capacity == 0)
break;
// 排除负数情况
if (i + first_index < _check_index)
continue;
// 如果长度超过 capacity 则退出
if (i + first_index - _check_index >= output_.writer().available_capacity() && i + first_index >= _check_index)
{
break;
}
if (!_index_checker[i + first_index - _offset])
{
capacity--;
_buffer[i + first_index - _offset] = data[i];
_index_checker[i + first_index - _offset] = true;
_reassemble_size++;
}
if (i + first_index == _check_index)
{
write_flag = true;
}
}
if (write_flag)
{
write_to_output();
}
if (is_last_substring)
{
_end_index = first_index + data.size();
}
if (_end_index == _check_index)
{
output_.writer().close();
}
}
uint64_t Reassembler::bytes_pending() const
{
return _reassemble_size;
}
void Reassembler::buffer_update()
{
_offset = _check_index;
for(uint64_t i = 0; i < _reasse_vector_size; i++)
{
_index_checker[i] = false;
}
for(uint64_t i = _check_index; i < _reasse_vector_size; i++)
{
_index_checker[i - _check_index] = _index_checker[i];
_buffer[i - _check_index] = _buffer[i];
}
}
void Reassembler::write_to_output()
{
string tmp {};
uint64_t tmp_size = output_.writer().available_capacity();
for(uint64_t i = _check_index; _index_checker[i - _offset] ; i++)
{
if (tmp_size == 0)
break;
tmp += _buffer[i - _offset];
_check_index++;
_reassemble_size--;
tmp_size--;
}
output_.writer().push(tmp);
}
reassembler.hh
#pragma once
#include "byte_stream.hh"
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#define _reasse_vector_size 152548
class Reassembler
{
public:
// Construct Reassembler to write into given ByteStream.
explicit Reassembler( ByteStream&& output ) : output_( std::move( output ) ) {
_buffer.resize(_reasse_vector_size);
}
/*
* Insert a new substring to be reassembled into a ByteStream.
* `first_index`: the index of the first byte of the substring
* `data`: the substring itself
* `is_last_substring`: this substring represents the end of the stream
* `output`: a mutable reference to the Writer
*
* The Reassembler's job is to reassemble the indexed substrings (possibly out-of-order
* and possibly overlapping) back into the original ByteStream. As soon as the Reassembler
* learns the next byte in the stream, it should write it to the output.
*
* If the Reassembler learns about bytes that fit within the stream's available capacity
* but can't yet be written (because earlier bytes remain unknown), it should store them
* internally until the gaps are filled in.
*
* The Reassembler should discard any bytes that lie beyond the stream's available capacity
* (i.e., bytes that couldn't be written even if earlier gaps get filled in).
*
* The Reassembler should close the stream after writing the last byte.
*/
void insert( uint64_t first_index, std::string data, bool is_last_substring );
// How many bytes are stored in the Reassembler itself?
uint64_t bytes_pending() const;
// Access output stream reader
Reader& reader() { return output_.reader(); }
const Reader& reader() const { return output_.reader(); }
// Access output stream writer, but const-only (can't write from outside)
const Writer& writer() const { return output_.writer(); }
uint64_t _check_index = 0;
private:
ByteStream output_; // the Reassembler writes to this ByteStream
uint64_t _reassemble_size = 0;
uint64_t _offset = 0;
uint64_t _end_index = 0xffffffff;
bool _index_checker[_reasse_vector_size] {0};
std::vector<char> _buffer {};
void write_to_output();
void buffer_update();
};